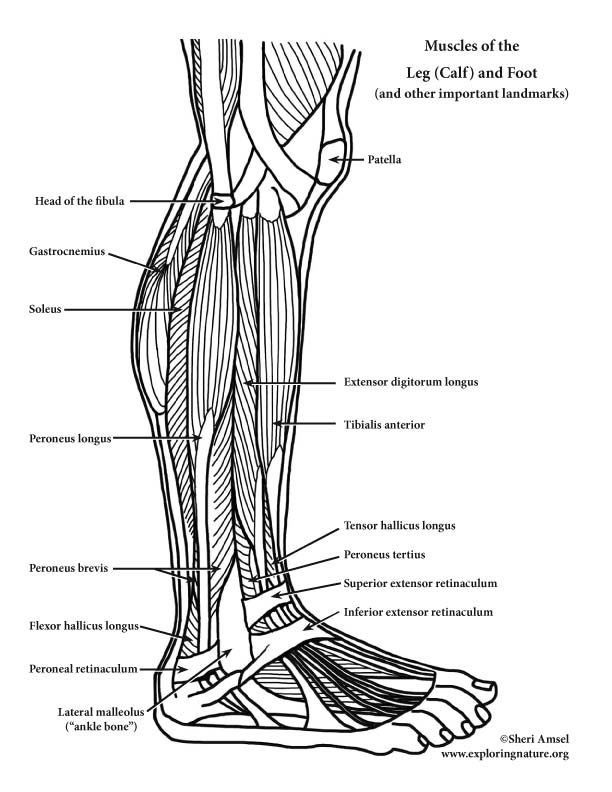
l. Anterior Compartment of Leg (Knee Down) – Dorsiflexion (Extension)
1) Tibialis anterior (shin splints muscle)
a. Actions: dorsiflexion, inverts foot (supports medial longitudinal arch)
b. Innervation: Deep peroneal nerve
c. Origin: from lateral condyle and upper tibia
d. Insertion: to medial cuniform bone (tarsal) and 1st metatarsal bone
2) Extensor digitorum longus
a. Actions: dorsiflexion, everts foot, extends toes
b. Innervation: Deep peroneal nerve
c. Origin: from lateral condyle and upper tibia and proximal fibula
d. Insertion: to 2nd and 3rd phalanges of toes 2-5
3) Peroneus tertius
a. Actions: dorsiflexion, everts foot
b. Innervation: Deep peroneal nerve
c. Origin: from distal and anterior fibula passes anterior to lateral malleolus
d. Insertion: on the dorsum of the 5th metatarsal
4) Extensor hallicus longus
a. Actions: extends great toe, dorsiflexion of foot, aids in foot inversion
b. Innervation: Deep peroneal nerve
c. Origin: from anterior, medial fibula
d. Insertion: to distal phalanx of big toe
ll. Muscles of the Lateral Compartment of Leg (Knee Down)
5) Peroneus longus
a. Actions: plantar flexion, everts foot
b. Innervation: Superficial peroneal nerve
c. Origin: from proximal fibula passes under foot
d. Insertion: to 1st metatarsal
6) Peroneus brevis
a. Actions: plantar flexion, everts foot
b. Innervation: Superficial peroneal nerve
c. Origin: from distal fibula passes behind lateral malleolus
d. Insertion: to insert proximally on 5th metatarsal
lll. Superficial Muscles of the Posterior Compartment of Leg (Knee Down)
7) Gastrocnemius
a. Actions: plantar flexion (when knee is extended), weak flexor of knee when foot is dorsifexed
b. Innervation: Tibial nerve
c. Origin: from medal and lateral condyles of femur
d. Insertion: to calcaneous via Achilles tendon (also called Calcaneal tendon)
8) Soleus
a. Actions: plantar flexion (at ankle) – locomotion muscle
b. Innervation: Tibial nerve
c. Origin: from tibia and fibula
d. Insertion: to calcaneous via Achilles tendon (also called Calcaneal tendon)
9) Plantaris
a. Actions: assists in knee flexion, plantar flexion of foot
b. Innervation: Tibial nerve
c. Origin: from posterior femur laterally
d. Insertion: to calcaneous via Achilles tendon (also called Calcaneal tendon)
lV. Deep Muscles of the Posterior Compartment of Leg (Knee Down)
10) Popliteus
a. Actions: flexes knee and rotates leg medially to unlock knee from full extension
b. Innervation: Tibial nerve
c. Origin: from lateral condyles of femur
d. Insertion: to proximal tibia
11) Flexor digitorum longus
a. Actions: plantar flexes foot, inverts foot, flexes toes (helps foot grip ground)
b. Innervation: Tibial nerve
c. Origin: from posterior tibia runs behind medial malleolus
d. Insertion: into 4 tendons to distal phalanges of toes 2-5
12) Flexor hallicus longus
a. Actions: plantar flexes foot, inverts foot, flexes big toe at all joints (pushes off during walking)
b. Innervation: Tibial nerve
c. Origin: from middle fibula runs under foot
d. Insertion: to distal phalanx of big toe
13) Tibialis posterior
a. Actions: inverts foot, plantar flexes foot (supports medial longitudinal arch)
b. Innervation: Tibial nerve
c. Origin: from proximal tibia and fibula it runs behind medial malleolus under arch
d. Insertion: into 4 tendons to tarsals and metatarsals 2-4
Not Muscle:
14) Superior extensor retinaculum
15) Inferior extensor retinaculum
16) Peroneal retinaculum
17) Lateral malleolus or “ankle bone”
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Use this study tool to learn the Muscles of the Leg (Calf) and Foot: Color the Muscles of the Leg (Calf) and Foot
Assess your knowlege of the Muscles of the Leg (Calf) and Foot: Label the Muscles of the Leg (Calf) and Foot
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Muscles of the Leg (Calf) and Foot (Lateral View) (Advanced)" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 13, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/Leg-Calf-and-Foot-Muscles-Lateral-View-Advanced >