Diagrams, Testing, Experiments & NGSS Links:
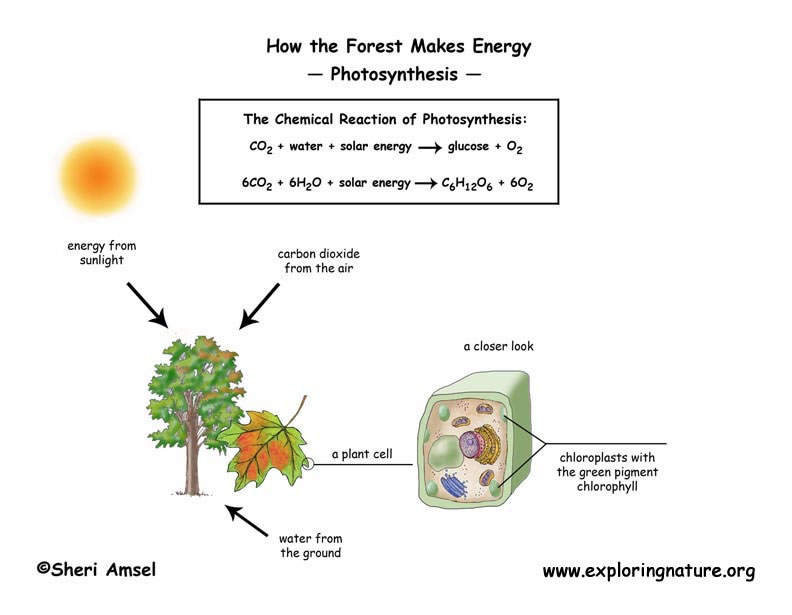
The leaf is the food-making part of a plant. Its structure is ideal for carrying out photosynthesis. The top and bottom surfaces of a leaf protect the cells inside. Xylem (tubes that carry water up from the roots) and phloem (tubes that carry food made in the leaves around the plant) are found in veins inside the leaf. Underneath the leaf are small openings called stomata. The stomata open and close to allow materials into and out of the leaf.
Chloroplasts are the parts (organelles) of plant cells, which contain chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is the green pigment that traps the light energy needed for photosynthesis to occur. The cells that contain the most chloroplasts are on the upper surface of a leaf exposed to the sun.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) enters the leaf through the stomata. Water is absorbed by the roots and moves up to the leaf through the xylem. The energy absorbed by the chlorophyll helps to change the carbon dioxide and water into sugar (glucose) and oxygen (O2). Oxygen is then released from the leaf through the stomata. Sugar then travels to other parts of the plant through the phloem. The plant uses the sugars to grow and reproduce.
The formula for photosynthesis is: Light + water + CO2 = Sugars + O2
See the PDF at bottom for:
Look at the diagrams below to see a visual image of the process of photosynthesis.
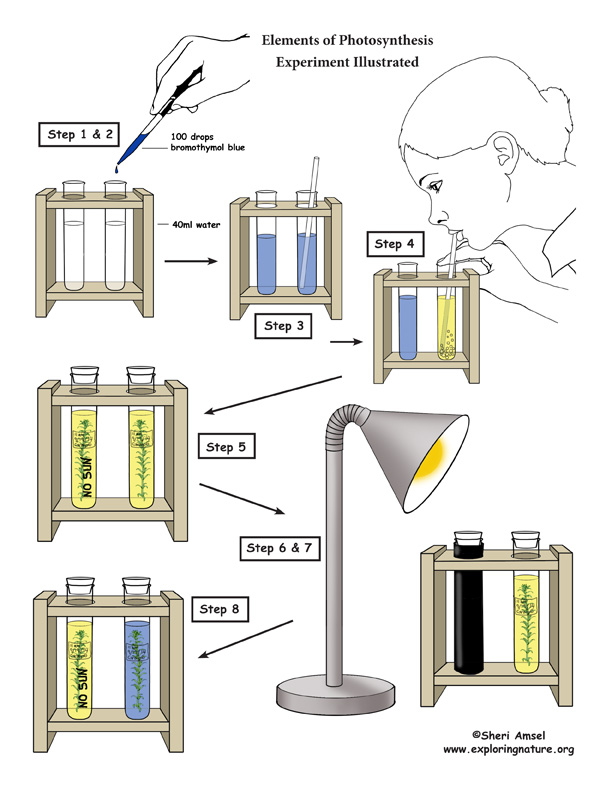
Experiment - The Elements of Photosynthesis
Goals: For photosynthesis to occur, a plant needs sunlight, water and carbon dioxide. To see photosynthesis in action, we will observe how a green plant (elodea) uses sunlight to take in CO2 and release O2 (control). In addition, we will deny sunlight to another specimen, to observe how photosynthesis does not occur without sunlight. Follow the procedures below to complete this experiment.
Materials:
(two per group) test tubes, stoppers, straws
(one per group) wax pencil, scissors, eye droppers, measuring beaker
specimens of elodea (from local pet store)
light source (grow light or sunny window)
bromothymol blue (BTB) as a CO2 indicator
tap water that has sat out for at least 24 hours (chlorine will evaporate)
black construction paper and tape
Procedures:
Break students down into groups of 3-4 with each group getting a set of two test tubes. Students in each group should take turns completing each of the following steps in each group.
1. Measure 40ml of the prepared tap water into each of their two test tubes.
2. Using the eye dropper, add about 100 drops of the bromothymol blue into each of the test tubes.
Important Fact: Bromothymol blue is used as an indictor for the presence of carbon dioxide.
3. Using a separate straw for each test tube, mix the water and bromothymol blue in each of the test tubes (leaving the straws in each test tubes afterward).
Thinking Moment: How can you add CO2 to the test tubes?
4. Doing one test tube at a time, cover the top with a finger to prevent splashing and then gently blow carbon dioxide into the test tube through the straw until the liquid turns yellow.
Discuss what the change in color indicates about the contents of the test tubes.
5. Cut a small sprig of elodea using scissors (make an angular cut in the stem) and place the plant bit in each of the test tubes. Then stopper them. Label each with the time, date and group number.
6. Add the words “no sun” to one of the test tubes using the wax pencil and wrap it with black construction paper, taping it in place so that no sunlight can get in.
7. Place both test tubes in a holder in front of a light source (sunny window or grow light) so that they both get the same amount of warmth even though one will get no light.
Thinking Moment: Can you predict what will happen over the next few hours? Discuss.
8. Several hours later (or next class period), have students remove the black paper from their test tube and compare the color of both liquids in the two test tubes.
Observation: Explain what changed in the test tubes.
Critical Thinking:
A. Explain what happened in this experiment.
B. Using the formula for photosynthesis explain how you simulated each part:
water + CO2 + sunlight = O2 + glucose
See the PDF at bottom for:
Vll. Summarize Knowledge - Enduring Understandings
1) Plants need sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy (in the form of glucose).
2) The ability of plants to produce energy from the sun (water and CO2) is the basis of all the food webs on Earth.
3) The ability of plants to produce oxygen from the sun (water and CO2) is the basis of all oxygen breathing life on Earth.
Vlll. NGSS and Common Core Integration
MS.Matter and Energy in Organisms and Ecosystems
Disciplinary Core Ideas:
LS1.C Organization for matter and energy flow in organisms
• Plants, algae (including phytoplankton), and many microorganisms use the energy from light to make sugars (food) from carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and water through the process of photosynthesis, which also releases oxygen. These sugars can be used immediately or stored for growth or later use. (MS-LS1-6)
• Within individual organisms, food moves through a series of chemical reactions in which it is broken down and rearranged to form new molecules, to support growth, or to release energy. (MS-LS1-7)
PS3.D Energy in chemical processes and everyday life
3-5 Sunlight warms Earth’s surface. Energy can be “produced,” “used,” or “released” by converting stored energy. Plants capture energy from sunlight, which can later be used as fuel or food.
6-8 Sunlight is captured by plants and used in a reaction to produce sugar molecules, which can be reversed by burning those molecules to release energy.
Crosscutting Concepts:
Cause and Effect
• Cause and effect relationships may be used to predict phenomena in natural or designed systems. (MS-LS2-1)
Energy and Matter
• Matter is conserved because atoms are conserved in physical and chemical processes. (MS-LS1-7)
• Within a natural system, the transfer of energy drives the motion and/or cycling of matter. (MS-LS1-6)
• The transfer of energy can be tracked as energy flows through a natural system. (MS-LS2-3)
Stability and Change
• Small changes in one part of a system might cause large changes in another part. (MS-LS2-4)
Science and Engineering Practices:
Developing and Using Models
Modeling in 6–8 builds on K–5 experiences and progresses to developing, using, and revising models to describe, test, and predict more abstract phenomena and design systems.
• Develop a model to describe phenomena. (MS-LS2-3)
• Develop a model to describe unobservable mechanisms. (MS-LS1-7)
Analyzing and Interpreting Data
Analyzing data in 6–8 builds on K–5 experiences and progresses to extending quantitative analysis to investigations, distinguishing between correlation and causation, and basic statistical techniques of data and error analysis.
• Analyze and interpret data to provide evidence for phenomena. (MS-LS2-1)
Constructing Explanations and Designing Solutions
Constructing explanations and designing solutions in 6–8 builds on K–5 experiences and progresses to include constructing explanations and designing solutions supported by multiple sources of evidence consistent with scientific knowledge, principles, and theories.
• Construct a scientific explanation based on valid and reliable evidence obtained from sources (including the students’ own experiments) and the assumption that theories and laws that describe the natural world operate today as they did in the past and will continue to do so in the future. (MS-LS1-6)
Engaging in Argument from Evidence
Engaging in argument from evidence in 6–8 builds on K–5 experiences and progresses to constructing a convincing argument that supports or refutes claims for either explanations or solutions about the natural and designed world(s).
• Construct an oral and written argument supported by empirical evidence and scientific reasoning to support or refute an explanation or a model for a phenomenon or a solution to a problem. (MS-LS2-4)
Performance Expectations:
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
MS-LS1-6. Construct a scientific explanation based on evidence for the role of photosynthesis in the cycling of matter and flow of energy into and out of organisms. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on tracing movement of matter and flow of energy.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include the biochemical mechanisms of photosynthesis.]
MS-LS1-7. Develop a model to describe how food is rearranged through chemical reactions forming new molecules that support growth and/or release energy as this matter moves through an organism. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on describing that molecules are broken apart and put back together and that in this process, energy is released.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include details of the chemical reactions for photosynthesis or respiration.]
MS-LS2-1. Analyze and interpret data to provide evidence for the effects of resource availability on organisms and populations of organisms in an ecosystem. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on cause and effect relationships between resources and growth of individual organisms and the numbers of organisms in ecosystems during periods of abundant and scarce resources.]
MS-LS2-3. Develop a model to describe the cycling of matter and flow of energy among living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on describing the conservation of matter and flow of energy into and out of various ecosystems, and on defining the boundaries of the system.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include the use of chemical reactions to describe the processes.]
MS-LS2-4. Construct an argument supported by empirical evidence that changes to physical or biological components of an ecosystem affect populations. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on recognizing patterns in data and making warranted inferences about changes in populations, and on evaluating empirical evidence supporting arguments about changes to ecosystems.]
Common Core State Standards Connections:
ELA/Literacy -
RST.6-8.1 Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of science and technical texts. (MS-LS1-3),(MS-LS1-4),(MS-LS1-5),(MS-LS1-6)
RST.6-8.2 Determine the central ideas or conclusions of a text; provide an accurate summary of the text distinct from prior knowledge or opinions. (MS-LS1-5),(MS-LS1-6)
RI.6.8.7 Integrate quantitative or technical information expressed in words in a text with a version of that information expressed visually (e.g., in a flowchart, diagram, model, graph, or table). (MS-LS2-1)
WHST.6-8.1 Write arguments focused on discipline content. (MS-LS1-3),(MS-LS1-4)
WHST.6-8.2 Write informative/explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas, concepts, and information through the selection, organization, and analysis of relevant content. (MS-LS1-5),(MS-LS1-6)
WHST.6-8.7 Conduct short research projects to answer a question (including a self-generated question), drawing on several sources and generating additional related, focused questions that allow for multiple avenues of exploration. (MS-LS1-1)
WHST.6-8.9 Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. (MS-LS1-5),(MS-LS1-6)
SL.8.5 Integrate multimedia and visual displays into presentations to clarify information, strengthen claims and evidence, and add interest. (MS-LS1-2),(MS-LS1-7)
Mathematics -
6.EE.C.9 Use variables to represent two quantities in a real-world problem that change in relationship to one another; write an equation to express one quantity, thought of as the dependent variable, in terms of the other quantity, thought of as the independent variable. Analyze the relationship between the dependent and independent variables using graphs and tables, and relate these to the equation. (MS-LS1-6),(MS-LS2-3)
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Photosynthesis" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 13, 2024
< http://exploringnature.org/db/view/43 >